Enhancing Doctor-Patient Communication: 3 Key Strategies for Building Trust and Improving Healthcare Outcomes
By Nmami Agarwal 01-Jul 2023 Reading Time: 5 Mins
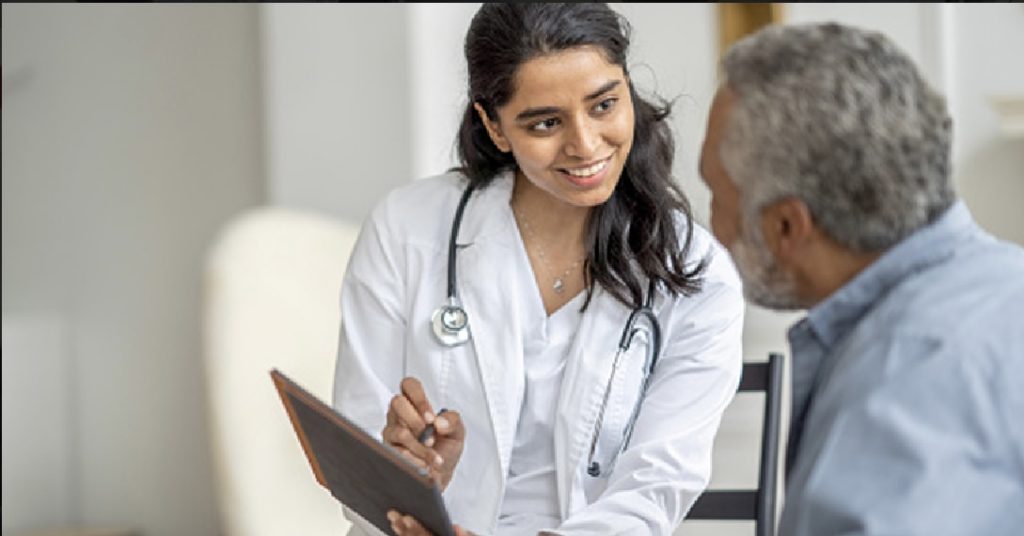

Introduction: Effective doctor-patient communication is a cornerstone of quality healthcare. It fosters trust and understanding and plays a vital role in improving healthcare outcomes. Building a solid doctor-patient relationship based on open and respectful communication empowers patients to participate actively in their care, leading to better treatment adherence and overall health outcomes. This article explores three key strategies to enhance doctor-patient communication and promote better healthcare experiences.
- Active Listening and Empathy:
Active listening:
- Doctors should practice active listening by paying complete attention to the patient’s concerns.
- This means maintaining eye contact, avoiding distractions, and refraining from interrupting.
- Active listening allows doctors to thoroughly comprehend patients’ needs and concerns, enabling them to provide appropriate care and treatment plans.
Empathy:
- Demonstrating empathy is crucial for establishing trust and rapport.
- Empathy involves understanding and sharing patients’ emotions, allowing doctors to provide compassionate care.
- Empathetic communication validates the patient’s experiences, making them feel heard and understood.
- By acknowledging their feelings, doctors can build stronger connections, ultimately enhancing patient satisfaction and treatment adherence.
- Use of Plain Language:
Simplify medical jargon:
- Doctors must effectively communicate complex medical information using plain language.
- Medical terminology can confuse and overwhelm patients, hindering their understanding of diagnoses, treatment options, and medication instructions.
- Doctors can bridge the communication gap by using clear and concise language and ensure patients comprehensively understand their health condition and the recommended treatment plan.
Visual aids and analogies:
- Visual aids, such as diagrams or illustrations, can be invaluable in simplifying complex medical concepts.
- Doctors can also employ analogies to explain medical terms or procedures by drawing parallels with everyday experiences.
- These techniques enable patients to grasp medical information more quickly, facilitating informed decision-making and treatment compliance.
- Shared Decision-Making:
Collaboration and respect:
- Doctors should embrace a collaborative approach involving patients in decision-making.
- Doctors should recognize that patients are experts in their own lives and respect their values, preferences, and goals.
- Doctors can foster a sense of ownership and partnership in decision-making by actively engaging patients in discussions about treatment options, potential risks, and benefits.
Patient education:
- Educating patients about their health conditions empowers them to participate in their care actively. Doctors should provide clear explanations, written materials, and reliable resources to enhance patients’ health literacy.
- Well-informed patients are more likely to adhere to treatment plans and make lifestyle changes, leading to better health outcomes.
Addressing doubts and concerns:
- Doctors should create a safe space for patients to express their doubts and concerns openly.
- By addressing these questions, doctors can alleviate anxiety, build trust, and strengthen the doctor-patient relationship.
- Encouraging patients to actively participate in discussions and ask questions fosters a sense of collaboration and shared responsibility for their healthcare.
Conclusion:
Enhancing doctor-patient communication is essential for building trust and improving healthcare outcomes. Doctors can establish stronger connections with their patients by implementing active listening and empathy strategies, using plain language, and promoting shared decision-making. Effective communication empowers patients to engage in their care actively, improving treatment adherence, health outcomes, and patient satisfaction. Emphasizing these strategies in medical practice benefits individual patients and contributes to a more patient-centered healthcare system overall.